The Hadoop Ecosystem is a framework and suite of tools that tackle the many challenges in dealing with big data. Although Hadoop has been on the decline for some time, there are organizations like LinkedIn where it has become a core technology. Some of the popular tools that help scale and improve functionality are Pig, Hive, Oozie, and Spark. Spark has developed legs of its own and has become an ecosystem unto itself, where add-ons like Spark MLlib turn it into a machine learning platform that supports Hadoop, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos.
Most of the tools in the Hadoop Ecosystem revolve around the four core technologies, which are YARN, HDFS, MapReduce, and Hadoop Common. All these components or tools work together to provide services such as absorption, storage, analysis, maintenance of big data, and much more.
Here is a list of the key components in Hadoop:
- HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System
- HIVE: Data warehouse that helps in reading, writing, and managing large datasets
- PIG: helps create applications that run on Hadoop, allowing to execute jobs in MapReduce
- MapReduce: System used for processing large data sets
- YARN: Yet Another Resource Negotiator
- Spark: Popular analytics engine that works in-memory
- Oozie: Open-source workflow scheduling program
- Zookeeper: Centralized service for maintaining config info, naming, providing distributed synchronization, and more
- Mahout: Helps create ML applications
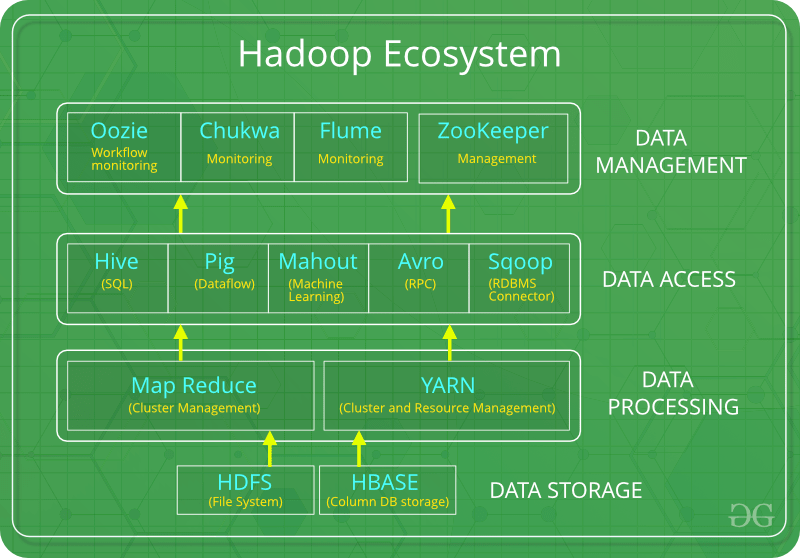
Source: Hadoop Ecosystem
Below, we highlight the various features of Hadoop.
MapReduce
Hadoop MapReduce is a software programming model used for writing applications. These applications can process multi-terabyte data-sets in-parallel on large clusters of commodity hardware in an Apache Hadoop cluster in a fault-tolerant manner.
MapReduce improves the reliability and speed of this parallel processing and massive scalability of unstructured data stored on thousands of commodity servers.
Two main functions of MapReduce are:
- Map (): Performs actions like grouping, filtering, and sorting on a data set. The result is a key-value pair (K, V) that acts as the input for Reduce function.
- Reduce (): Aggregates and summarizes the outputs of the map function. The Reduce function combines data tuples according to the key and modifies the key’s value.
The HDFS architecture (Hadoop Distributed File System) and the MapReduce framework run on the same set of nodes because both storage and compute nodes are the same.
Due to this configuration, the framework can effectively schedule tasks on nodes that contain data, leading to support high aggregate bandwidth rates across the cluster.
Top benefits of MapReduce are:
- Simplicity: MapReduce jobs are easy to run. Developers can write applications in any programming language such as C++, Java, and Python.
- Scalability: Can process petabytes of data.
- Speed: Parallel processing reduces time to hours and minutes for jobs that often take days to solve.
- Fault Tolerance: Takes care of failures. If one data copy is unavailable, another machine with the same key pair kicks in to solve the same task.
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator)
Introduced in Hadoop 2.0 to remove the bottleneck on Job Tracker, YARN has now evolved to be a large-scale distributed operating system for Big Data processing.
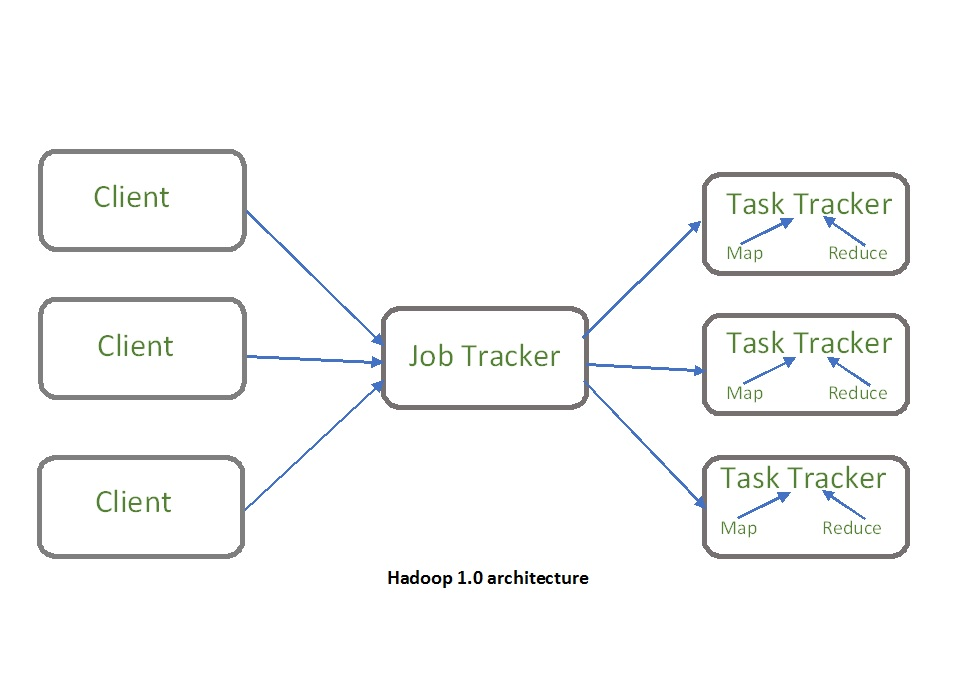
In Hadoop 1.0, the Job tracker’s functionalities are divided between the application manager and resource manager. However, the YARN architecture separates the processing layer from the resource management layer. There is a global ResourceManager (RM) and per-application ApplicationMaster (AM).
The data-computation framework is made of the ResourceManager and the NodeManager. The ResourceManager arbitrates resources among all available applications, whereas the NodeManager is the per-machine framework agent. The latter is responsible for monitoring and reporting the resource usage of containers to the ResourceManager/Scheduler.
The ResourceManager consists of two main components: ApplicationsManager and Scheduler. The per-application ApplicationMaster handles the negotiation of resources from the ResourceManager. It also works with the NodeManager(s) to monitor and execute the tasks.
The Scheduler allocates resources to running applications with familiar constraints of queues, capacities, and other features. The Scheduler considers the resource requirements of the applications for scheduling, based on the abstract notion of a resource container that incorporates memory, disk, CPU, network, etc.
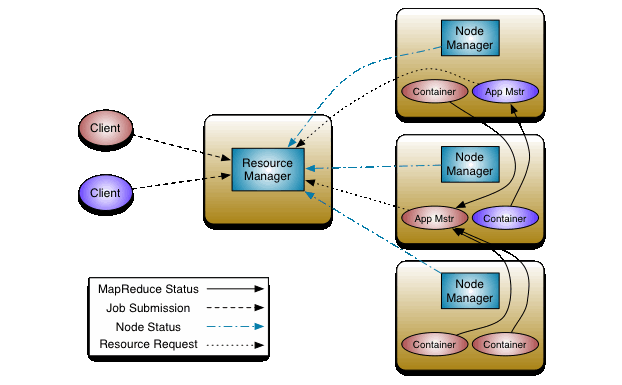
source: MapR
Key benefits of YARN are:
- Scalability: The scheduler allows Hadoop to extend and manage thousands of nodes and clusters.
- Compatibility: Supports existing MapReduce applications without disruptions, making it compatible with Hadoop 1.0.
- Cluster Utilization: YARN supports the dynamic utilization of clusters in Hadoop that allows optimized Cluster Utilization.
- Multi-tenancy: YARN architecture allows multiple engine access, allowing organizations to benefit from multi-tenancy.
Hive
Apache Hive was developed by Facebook for seasoned SQL developers. With this component, SQL developers can write Hive Query Language statements like standard SQL statements.
Basically, Apache Hive is a Hadoop-based open-source data warehouse system that facilitates easy ad-hoc queries and data summarization. It also enables the quick analysis of large datasets stored on various file systems and databases integrated with Apache Hadoop.
Hive provides SQL developers with a simple way to write Hive Query Language (HQL) statements that can be applied to a large amount of unstructured data. The objective of Hive is to make MapReduce programming easier as you don’t have to write lengthy Java code. You write queries simply in HQL, and it automatically translates SQL-like queries into batch MapReduce jobs.
You can easily integrate with traditional database technologies using the JDBC/ODBC interface.
Key benefits of Hive are:
- Shared Metastore and Data: Acts as a relational datastore for Spark in machine learning, predictive analytics, and other programming models via SparkSQL or API access. The metastore in Hive helps maintain metadata about Hive tables, making it programmatically available to developers.
- Data Warehouse Optimization: Used to optimize, augment, or even replace a traditional data warehouse with new-generation big data warehouses.
- Rich Processing Ecosystem for Data Mining: Core open-source projects and optimized native services benefit Hive-on-MapR users.
- Data Integration: Hive is increasingly being used for reducing the time and cost needed for the ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) process.
Pig
Apache Pig was developed by Yahoo and it enables programmers to work with Hadoop datasets using an SQL-like syntax. Presently, the infrastructure layer has a compiler that produces sequences of Map-Reduce programs using large-scale parallel implementations.
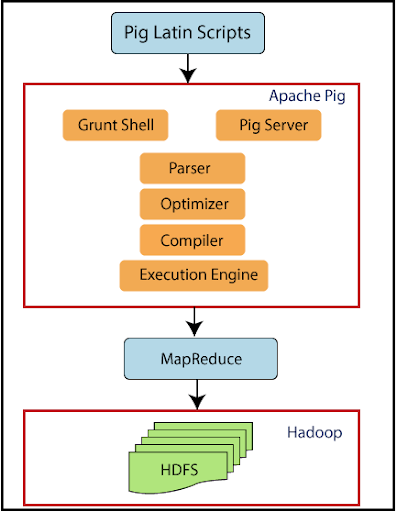
Pig Hadoop framework consists of four main components, including Parser, optimizer, compiler, and execution engine.
Parser handles the Pig Latin script when it is sent to Hadoop Pig. This component checks the syntax of the script and other miscellaneous checks. Parser’s output is in the form of DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), and it contains Pig Latin statements and other logical operators.
Once the output is retrieved, a plan for DAG is sent to a logical optimizer that carries out the logical optimizations. Next, the compiler compiles the logical plan sent by the optimizer and converts it into a sequence of MapReduce jobs.
These jobs are then passed to Hadoop in a sorted order where these are executed to get the desired result.
Top features of Pig are:
- In-built operators: Provides good operators for performing data operations like filter, sort, join, etc.
- Ease of programming: Pig’s language layer consists of a textual language known as Pig Latin. The top features of this language are ease of programming, optimization opportunities, and extensibility.
- Automatic optimization: Automatically optimizes tasks, allowing programmers to focus only on the language semantics.
- Handles all kinds of data: Analyze’s both structured and unstructured data and store the results in HDFS.
Spark
Originally developed at UC Berkeley, Apache Spark is an ultra-fast unified analytics engine for machine learning and big data. Internet giants such as Yahoo, Netflix, and eBay have deployed Spark at a large scale, to process petabytes of data on clusters of more than 8,000 nodes.
Spark is primarily used for in-memory processing of batch data. It also supports stream processing by combining data streams into smaller batches and running them. The component is generally used for machine learning because these algorithms are iterative and Spark is designed for the same.
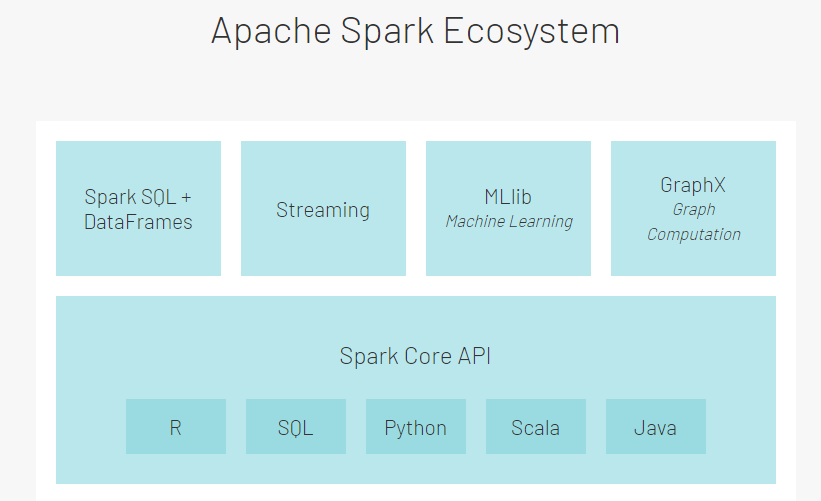
Top features of Apache Spark are:
- Speed: 100x faster compared to Hadoop, making it ideal for large scale data processing.
- Ease of Use: Easy-to-use APIs for smooth operations of large datasets. More than 100 operators transform data and familiar data frame APIs to manipulate semi-structured data.
- Unified Engine: Spark packages higher-level libraries, including support for streaming data, machine learning, SQL queries, and graph processing. Thus, it increases developer productivity and seamlessly combines to ease complex workflows.
Oozie
Apache Oozie is a Java-based open-source project that simplifies the process of workflows creation and coordination. It is fully integrated with the Apache Hadoop stack. Also, it supports Hadoop jobs for Apache MapReduce, Hive, Sqoop, and Pig.
An Oozie workflow is a collection of actions arranged in a DAG that can contain two different types of nodes: action nodes and control nodes. Control nodes define job chronology, provide the rules for a workflow, and control the workflow execution path with a fork and join nodes. On the other hand, action nodes trigger task execution. Action nodes can be MapReduce jobs, file system tasks, Pig applications, or Java applications.
The following diagram shows the Oozie Action execution model:
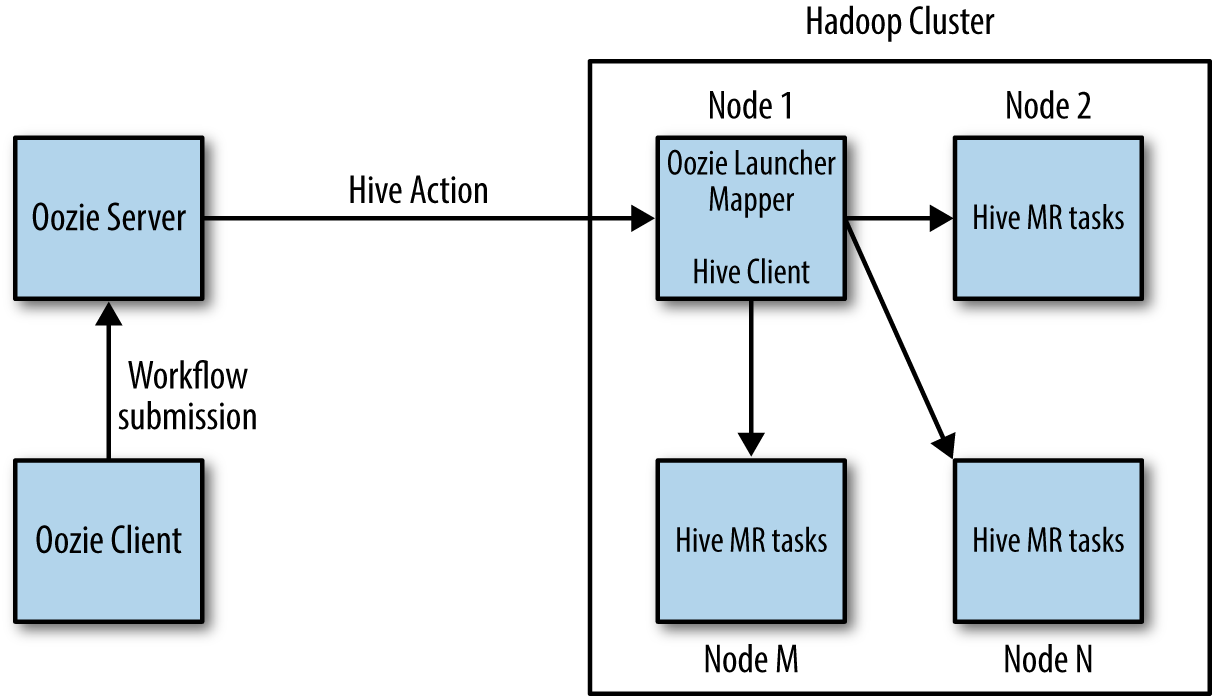
Oozie uses the XML-based language, Hadoop Process Definition Language, to define the workflow. This command-line program with Oozie uses REST to interact with Oozie servers. To run a job using the Oozie client, users give Oozie the full path to your workflow.xml file in HDFS as a client parameter. It uses an RDBMS for storing state.
Top features of Oozie are:
- Scale in a Hadoop cluster: Each job is launched from a different data node, allowing a balanced workflow load so that no single machine is overburdened.
- Built-in Hadoop actions: Makes workflow development, troubleshooting, and maintenance easier.
- Triggering actions: Oozie Coordinator allows triggering actions as files arrive at HDFS.
Zookeeper
This is an open-source Apache project that provides configuration information, synchronization, and group services and naming over large clusters in a distributed system. Zookeeper makes distributed systems easier to manage with more reliable changes propagation.
For applications, the project maintains status-type information called znode in the memory of Zookeeper servers. Then, it provides an infrastructure that allows cross-node synchronization.
Servers maintain and store a copy of the system’s state in local log files. Multiple Zookeeper servers are used to support large Hadoop clusters, where a master server synchronizes top-level servers.
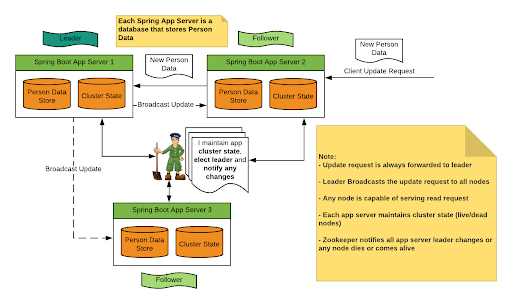
Top features of Zookeeper are:
- Data consistency: All update requests are forwarded to the leader who then broadcasts data to all active servers and responds with the updated status.
- No inconsistencies: Data is readable from any replicas without inconsistencies.
- Fast: It is fast with workloads where data reads are more common than writes.
Mahout
Apache Mahout is a powerful open-source machine-learning library that runs on Hadoop MapReduce. More specifically, Mahout is a mathematically expressive scala DSL and linear algebra framework that allows data scientists to quickly implement their own algorithms.
Companies such as Twitter, Adobe, LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Yahoo, and Foursquare, use Apache Mahout internally for various purposes.
The three main components of Mahout are the recommendation engine, clustering, and classification.
The recommendation engine supports the classification of item-based or user-based models. Facebook and Amazon use it to suggest products by mining user behavior.

Clustering makes a cluster of similar things using algorithms like Dirichlet Classification, Fuzzy K-Means, Mean Shift, Canopy, etc. Google’s Summly uses this feature to show the news from different news sites:
Finally, classification determines whether a thing should be a part of some predetermined type or not. Facebook’s spam checker and face detection use this technique.
Key features of Mahout are:
- Collaborative filtering: Mines user behavior to make product suggestions.
Ready-to-use framework: Allowing coders to easily do data mining on large data volumes. - Frequent pattern mining: Analyzes items in a group and identifies which items appear together.
Kube2Hadoop
LinkedIn developed Kube2Hadoop that integrates the authentication method of Kubernetes with the Hadoop delegation tokens. It does this while respecting the fine-grained role-based access control (RBAC). RBAC controls user access to its extensive Hadoop resources.
Three main components of Kube2Hadoop are:
- Kubernetes-resident Hadoop token service that fetches delegation tokens.
- Init container in each worker pod. It works as a client and sends requests for fetching delegation tokens from the Hadoop token service.
- An IDDecorator which writes an authenticated user-ID to be used as a Kubernetes admission controller.
Kube2Hadoop lets users working in a Kubernetes environment to access data from HDFS without compromising security.
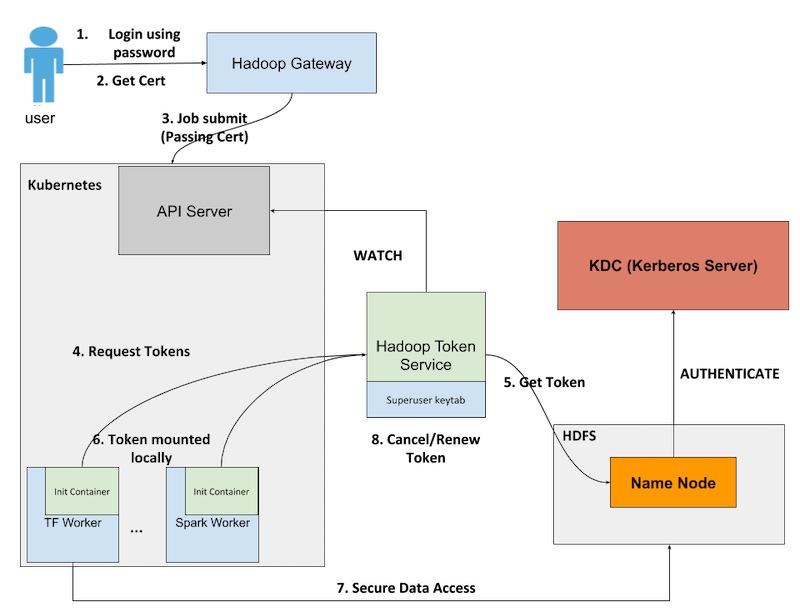
Key features of Kube2Hadoop are:
- Resistant to specific attacks: These specific attacks include user names in job annotation and Kubernetes pods.
- Cleaner access controls: Access controls to HDFS, Kube2Hadoop automatically renew tokens and ease the management of the token’s life cycle.
- Authenticates Users: The Kubernetes cluster authenticates users with the certificate to prevent malicious access.
Summary
The Hadoop Ecosystem is a powerful and highly scalable platform used by many large organizations. LinkedIn, Google, Facebook, MapR, Yahoo, and many others have contributed to improving its capabilities. While it might not be winning against the cloud-based offerings, it still has its place in the industry, in that it is able to solve specific problems depending on the use case.