When it comes to on-prem hardware, Dell and HPE are the industry juggernauts. According to IDC, “traditional spending” which is defined as “anything that’s not a private or public cloud” was 49.8% of total spending in 2019. That means half of IT spending was being invested in traditional IT.
There are many reasons why companies continue to buy hardware and software for their data centers: regulation, security, control, and so on. One of the reasons the large cloud providers have developed their own on-prem offering is to capture more of the traditional IT spend, by extending their cloud functionality to customer environments.
In some cases, on-prem environments provide better security and more control over data and processes, a requirement for some traditional enterprises and verticals. The caveat, on-prem means users are responsible for the operation and maintenance of the hardware and software. Microsoft, Google, and Amazon have created new on-prem cloud offerings to meet the needs of this segment, providing companies a consistent platform from the cloud to on-prem.
AWS Outposts
Amazon’s AWS Outposts is a private cloud hardware stack that can be installed on-prem such as the customer data center. This fully-managed service extends AWS infrastructure to any on-prem environment. It’s ideal for use cases that require low-latency computation. AWS Outposts offers pre-configured hardware and software that includes servers, storage, software stack, power supplies, and network switches.
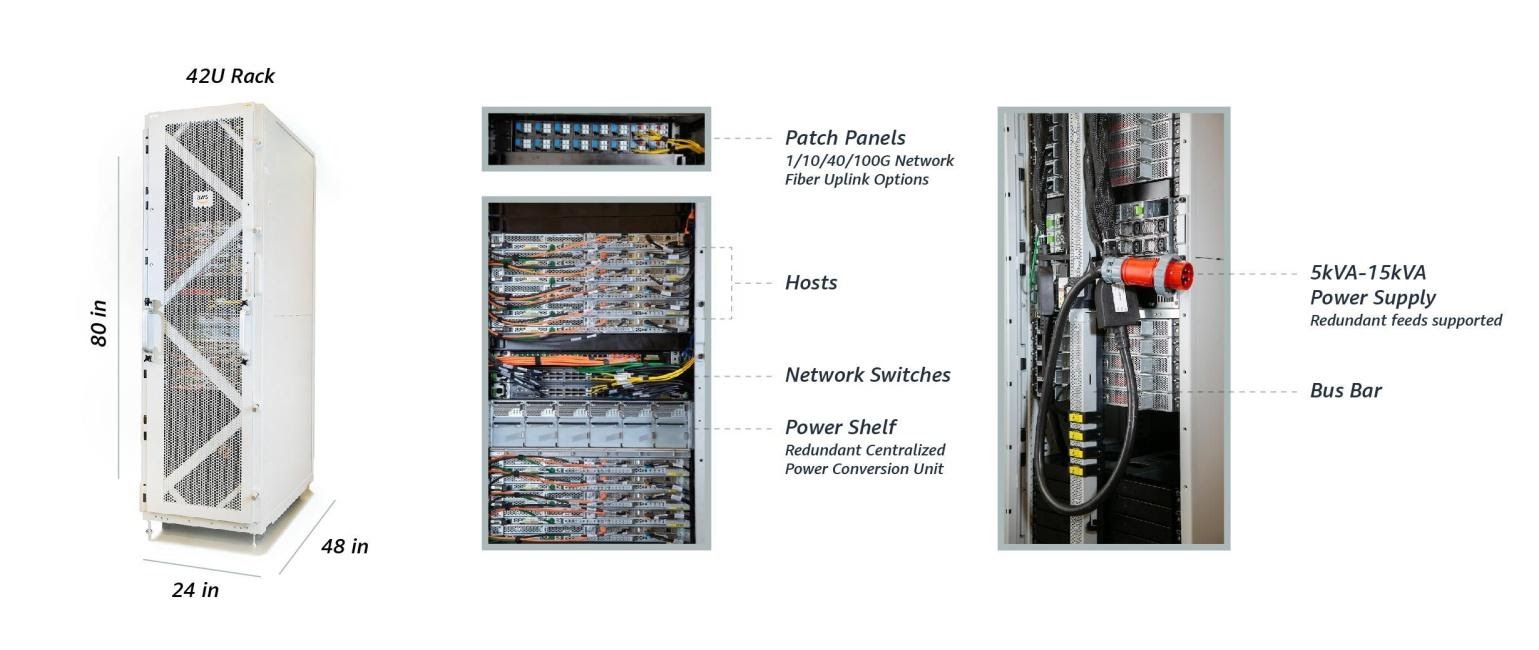
For users that require low-latency performance, AWS Outposts is an ideal product that allows companies to run Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) on-prem. Amazon plans on adding S3 storage soon.
- AWS Outposts for Versatile APIs and Services
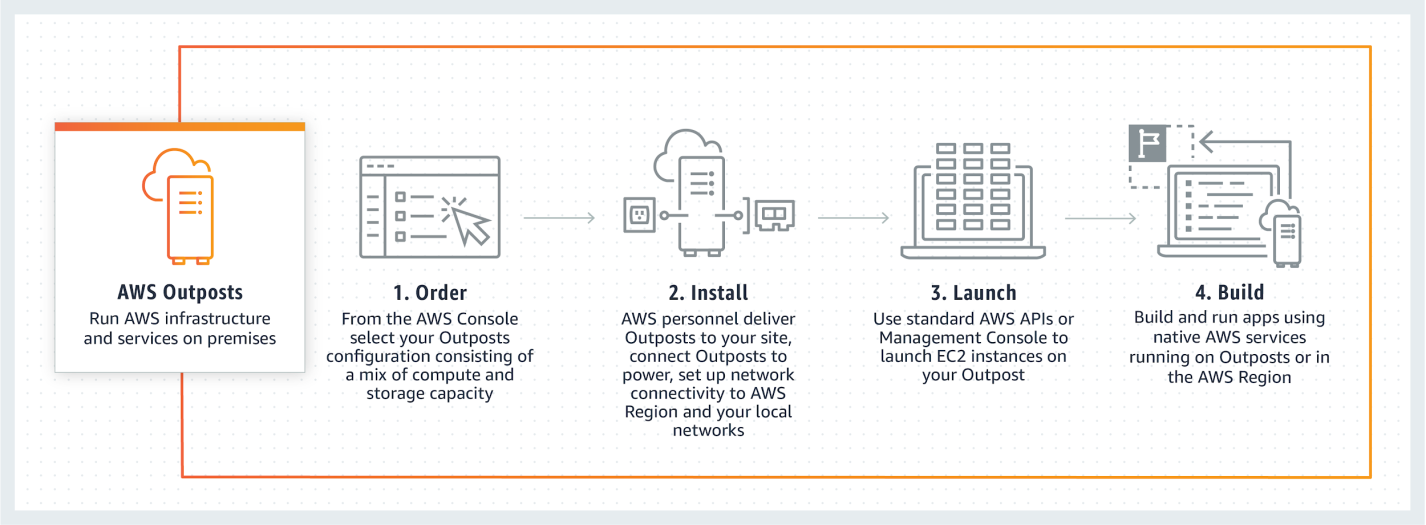
AWS Outposts extends its APIs, services, and tools to on-prem environments including the data center, physical servers, and combined workspace. The combined unit of hardware and software works as the central control plane to run AWS services locally. It also helps connect on-prem resources to APIs, security service centers, and management tools in the AWS cloud. Services like authentication, automation, management, monitoring, and security capabilities are available in this product.
- Versions of AWS Outpost
AWS Outposts come in two versions: AWS native Outposts and AWS Outposts on VMware Cloud. The native version was launched at AWS re:Invent 2019, which is entirely managed by AWS.
The second version, which is VMware Cloud, runs VMware’s data center and enables customers to use its control planes as well as APIs. VMware on AWS Cloud is gaining popularity as a hybrid cloud service because it offers a streamlined approach to shifting applications to the public cloud.
- Features of AWS Outposts
AWS Outposts support Intel-powered EC2 instance and Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes for big data storage, providing restore capabilities so users can increase volume size without affecting performance. Also, users may extend existing VPC capabilities to their environment via Outpost, as the service provides a local gateway (LGW) that enables low latency connectivity. AWS Outposts supports MySQL and PostgreSQL, eliminating the need to perform tasks such as maintenance, updates, patching, etc.
Google Anthos GKE
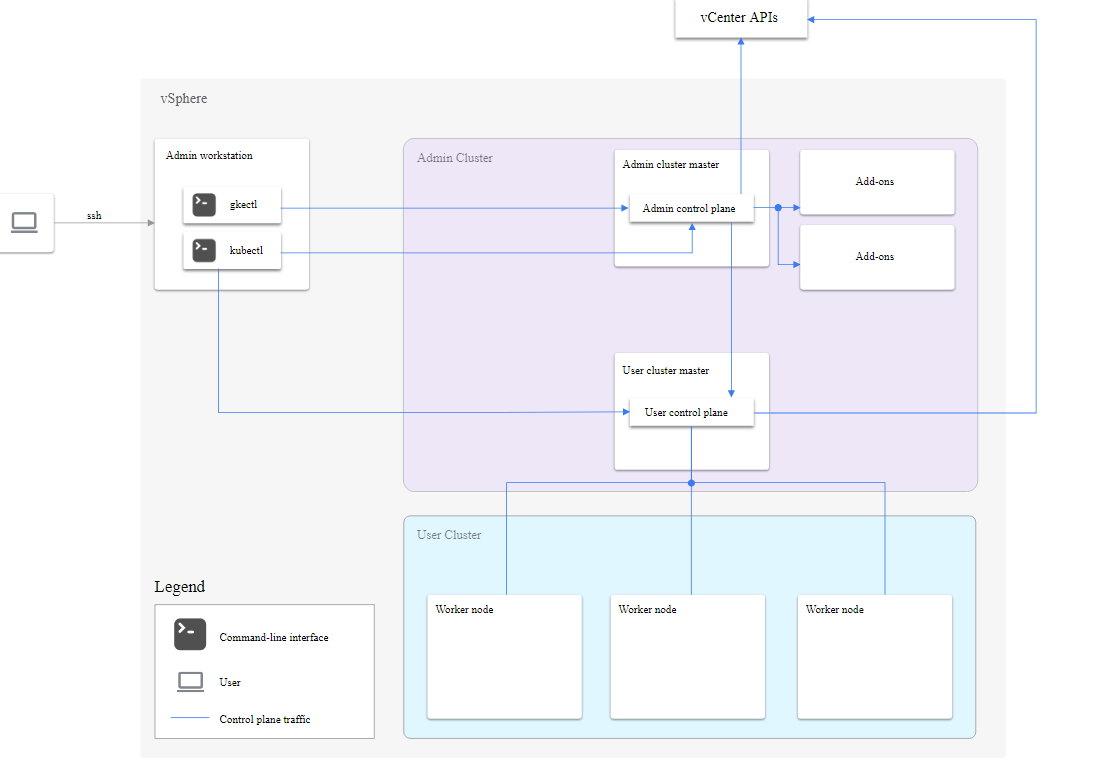
Anthos GKE marks Google’s entry into the on-prem segment and it allows customers to take advantage of Kubernetes in their data center environment. Users can build, deploy, and manage applications in a secure manner, as well as manage the Kubernetes ecosystem. The core component of this product is Anthos Migrate, which helps automate the migration of virtual workloads into Kubernetes containers. Google has collaborated with vendors such as Cisco, Dell, EMC, and NetApp to simplify this process.
Features of Anthos GKE
- Anthos GKE uses Istio, which is an open-source “service mesh” that secures communication between microservices. It also manages the traffic as well as API calls between services and third-party tools.
- With Anthos GKE, customers can move on-premise without shifting it to any other technologies.
- Other Anthos’ features include networking, service management, Centralized configuration, and monitoring the unified user interface.
Azure On-Prem Stack
Microsoft launched Azure Stack in 2017 and the service allows companies to use Azure services on-prem. This product comes in a hardware and software bundle that is tailored to a user’s specifications. The Azure stack comes with Blobs, tables, and queues, which are services available in the public cloud. Blob helps store unstructured data in the cloud and tables provide NoSQL storage to users that need to scale applications on-demand. Microsoft has also partnered with Cisco, HP, Huawei, Dell EMC, and Lenovo. Also, they announced the launch of a free Azure Stack development kit that provides all the core tools from the Azure portal and marketplace.
Features of Azure On-Prem Stack
- Companies can host and manage applications in a secure manner
- An organization can extend deployments from Azure public cloud to on-prem facilities
- Application frameworks like ASP.NET, Java, PHP, and Python are supported
- Microservices architecture is also supported
Summary: Platform Differences
- AWS Outposts and Azure are hardware and software-based solutions while Anthos GKE is software only
- AWS Outposts and Azure stack require hardware while Anthos GKE runs on existing hardware
- AWS Outposts and Azure Stack are limited to their cloud platforms. Anthos GKE supports 3rd party clouds
- AWS Outposts requires a minimum of one node to start with while Azure Stack requires a minimum of four nodes